- No.277 Shuangshan Road,Deqing,Zhejiang,CHINA
- [email protected]
- WhatsApp+8613065722186
Wound Healing Zip Stitch Wound Closure Device Steri Strip
Wound healing is a complex biological process that the body undergoes to repair damaged tissue, whether it’s from injury, surgery, or other causes. The primary goal of wound healing is to restore the integrity and function of the injured tissue, as well as to prevent infection.
Several factors can influence the speed and effectiveness of wound healing, including a person’s age, overall health, nutrition, and the size and type of wound. Some wounds may heal with minimal scarring, while others may result in more prominent scars. In certain cases, such as chronic wounds or wounds with underlying medical conditions, the healing process can be impaired and may require medical intervention.
What are the main processes of wound healing?
Hemostasis: This is the initial phase that begins immediately after tissue injury. It involves blood clot formation to stop bleeding. Platelets in the blood aggregate at the site of injury to form a temporary plug, and the blood coagulates to form a fibrin clot.
Inflammatory Phase: Following hemostasis, the body initiates an inflammatory response to clear out any debris, dead cells, and potential pathogens from the wound. This phase is characterized by the release of various inflammatory mediators, such as cytokines and chemokines, which attract immune cells like neutrophils and macrophages to the wound site.
Proliferative Phase: During this phase, new tissue is generated to replace the damaged or dead tissue. Fibroblasts produce collagen, a key protein that forms the structural framework for the healing tissue. New blood vessels, a process called angiogenesis, also develop to supply oxygen and nutrients to the healing area. Epithelial cells migrate across the wound surface to close it.
Remodeling Phase: In the final phase, the new tissue formed during the proliferative phase undergoes remodeling. Collagen is reorganized and strengthened, and the wound gradually regains its strength and flexibility. This phase can last for months to years, and the appearance of the scar may change during this time.
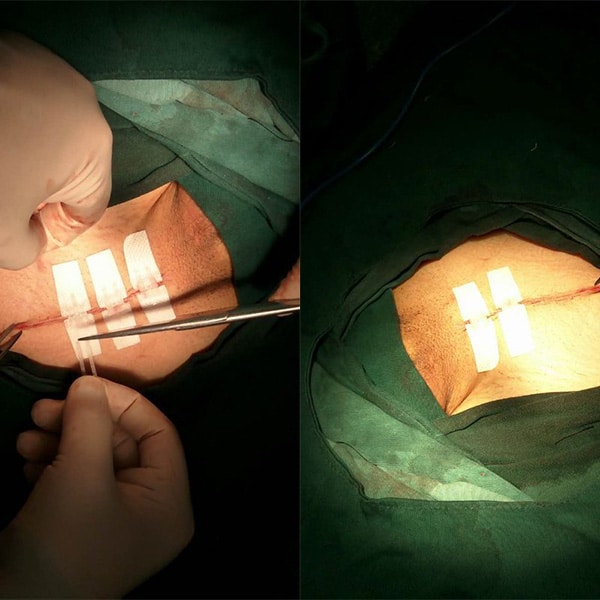
Longmed Zip Stich Wound Closure Device For Wound Healing
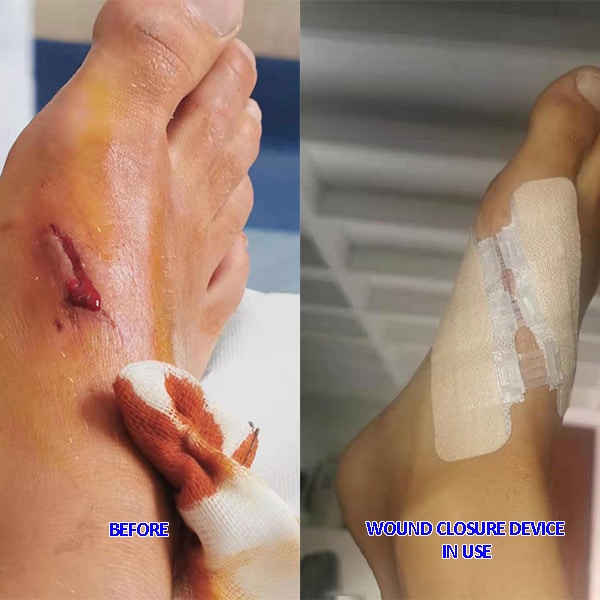
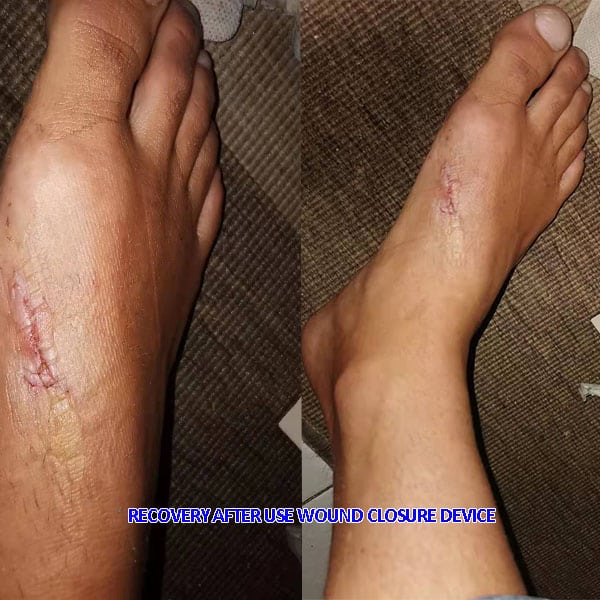
More Info About Wound Closure Device For Wound Healing
What are the main factors that influences the wound healing?
Wound healing is a complex process influenced by a variety of factors. These factors can broadly be categorized into intrinsic (internal) and extrinsic (external) factors. Here are the main factors that influence wound healing:
Intrinsic Factors:
Age: Wound healing tends to be slower in older individuals. Aging can lead to a decrease in the function of cells involved in the healing process, reduced blood flow to tissues, and a decline in collagen production.
Overall Health: The general health of an individual plays a significant role in wound healing. Chronic diseases such as diabetes, cardiovascular conditions, and immune disorders can impair the body’s ability to heal wounds.
Nutrition: Adequate nutrition is essential for wound healing. Proteins, vitamins (particularly vitamin C and vitamin A), minerals (such as zinc), and calories are all crucial for the body to generate new tissue and fight off infections.
Blood Supply: Sufficient blood flow to the wound site is critical for delivering oxygen and nutrients necessary for healing. Conditions that affect blood circulation, like peripheral vascular disease, can hinder the healing process.
Chronic Illnesses: Conditions like diabetes and autoimmune diseases can impair the immune response and blood flow to the wound, making healing more challenging.
Medications: Certain medications, such as corticosteroids and chemotherapy drugs, can interfere with the healing process or increase the risk of infection.
Extrinsic Factors:
Infection: The presence of bacteria, viruses, or other pathogens in a wound can significantly delay healing and lead to complications. Infections must be treated promptly.
Wound Care: Proper wound care, including cleaning, dressing changes, and protection from further injury, is crucial for optimal healing.
Smoking and Alcohol: Smoking can reduce blood flow and oxygen delivery to tissues, while excessive alcohol consumption can impair the immune system, both of which can hinder wound healing.
Stress: Chronic stress can negatively impact the immune system and slow down the healing process.
Obesity: Excess body weight can affect blood flow and increase the risk of wound complications.
Environmental Factors: Exposure to contaminants or irritants, such as chemicals or radiation, can impair wound healing.
Surgical Technique: The skill and technique of the surgeon or healthcare provider performing a procedure can influence the quality and speed of wound healing.
Foreign Bodies: The presence of foreign objects or debris in a wound can impede healing and increase the risk of infection.
Chronic Inflammation: Conditions that lead to chronic inflammation in the body, such as rheumatoid arthritis, can interfere with the normal wound healing process.
Hormones: Hormonal imbalances, such as those that occur during pregnancy or menopause, can affect wound healing.
It’s essential to consider these factors when assessing a wound and developing a treatment plan. Addressing any underlying health conditions and providing proper wound care are crucial steps in promoting optimal wound healing and reducing the risk of complications. Healthcare professionals play a vital role in managing and facilitating the healing process, especially for more complex or chronic wounds.
